June 8, 2016
June 8, 2016
As Phase I clinical trials mark the first time that an investigational new drug is administered to humans, these studies are subject to appropriate current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) in order to ensure patient safety.
In this blog we will explore cGMP compliance in the context of the of following functional areas.
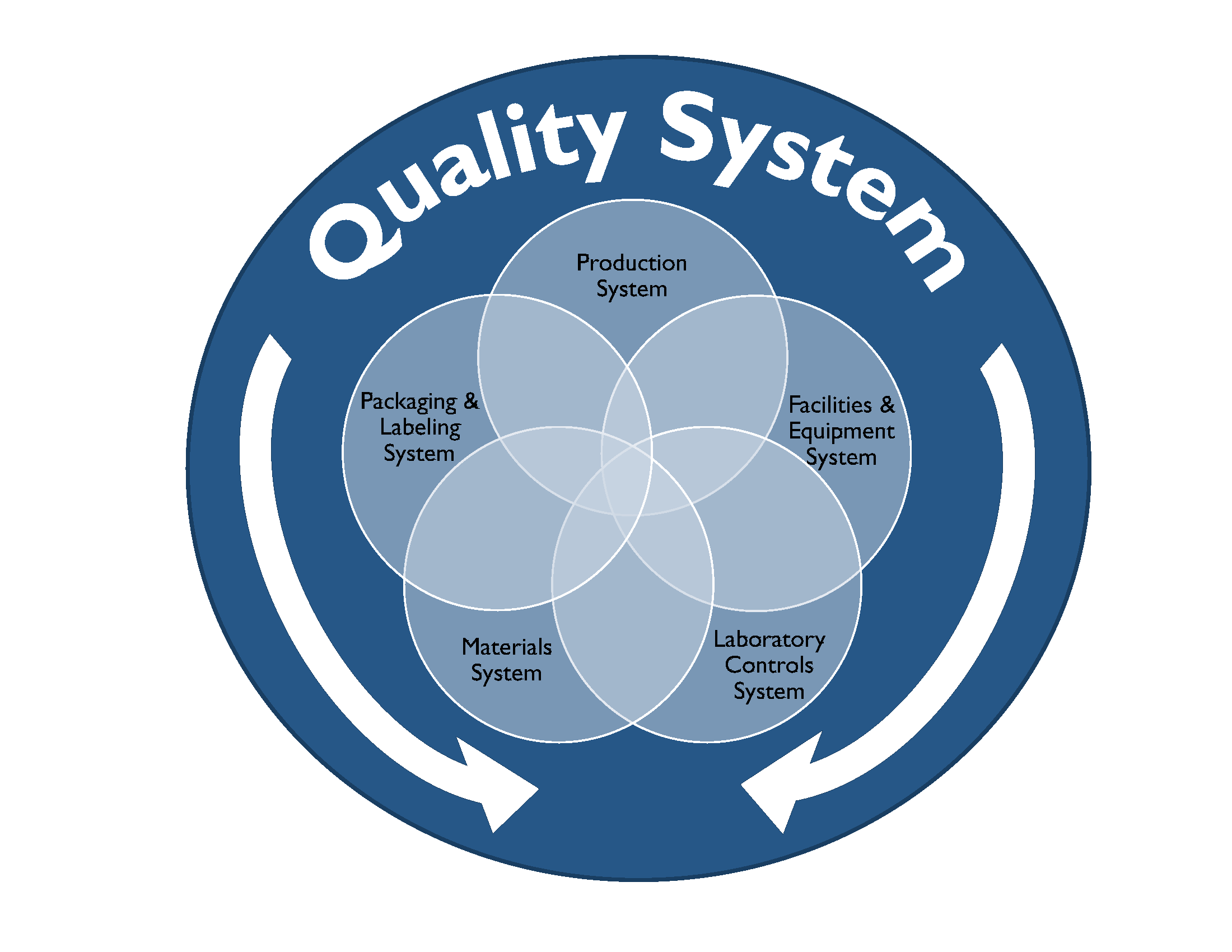
Compliance with cGMP during manufacture of Phase I investigational drug products is established using clearly documented procedures, effective control of the manufacturing setting with respect to product environment, equipment, personnel and materials to avoid potential hazards and well recorded data from all activities related to manufacture of the drug product and all in-process and finished product testing.
Well defined activities prior to and during manufacturing are performed in order to ensure the quality of the drug product. Personnel should be trained appropriately to perform the duties for which they are responsible. Facilities used for manufacture of Phase I investigational drug product should have the appropriate work areas and necessary equipment. Work areas should be clean and provide ample space, proper lighting, ventilation, HVAC systems, plumbing and air handling systems to prevent contamination of the finished drug product. All equipment used in the manufacture of Phase 1 drug product should be identified, well maintained, calibrated, and cleaned appropriately according to the associated written procedures and these processes should be documented in the manufacturing batch record.
The Quality Control (QC) department is responsible for testing and controlling raw materials, in-process samples, finished product release testing and also for investigating unexpected results or out of specification results. Test methods should follow written procedures to evaluate specific attributes such as identity, strength, potency, and purity. Clear documentation should be maintained for all procedures, test results, and revisions to procedures. A certificate of analysis (COA) is issued for each lot of drug product which demonstrates that the material meets specified acceptance criteria for each of the attributes examined. At this stage in the development pathway however, certain attributes or acceptance criteria may not have yet been defined. Representative samples of the manufactured drug product batch should be placed into a formal stability study, as per a clearly written protocol to evaluate the product attributes as a function of time, temperature and humidity. Manufacturers should have documentation in place that outlines the roles, responsibilities and training for QC personnel and also for calibration and maintenance of laboratory equipment as applicable.
The QA team is responsible for establishing and maintaining quality systems and reviewing out of specification results and any corrective and preventative actions implemented for release of finished product and maintaining the executed batch records, among many other functions. The batch record should describe the materials, component records, equipment, procedures used, and issues observed during manufacturing, including deviations and investigations and should be detailed enough to be able to successfully reproduce the manufacturing operation. The batch record should also document if a run was terminated and what the cause was.
The Phase 1 investigational drug product should be inspected and appropriately packaged as per defined procedures to protect it from contamination or damage during storage, handling, and distribution to clinical study sites in accordance with the conditions on the label.
In summary, manufacturers of clinical trial material should have at a minimum:
Learn more about ProPharma's Compliance services. Contact us to get in touch with our subject matter experts for a customized presentation.
December 4, 2014
Compounding is a practice in which a licensed pharmacist, a licensed physician, or, in the case of an outsourcing facility, a person under the supervision of a licensed pharmacist, combines, mixes,...

July 16, 2014
Compounding is a practice in which a licensed pharmacist, a licensed physician, or, in the case of an outsourcing facility, a person under the supervision of a licensed pharmacist, combines, mixes,...
September 2, 2014
In June 2014, the FDA issued two draft social media guidance documents that may not clearly answer all of the questions that the drug and device industries have about how to use social media to...